Over time, the Internet has improved and changed. This evolution is known as Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0.
The third generation of online technology, Web 3.0, is here to stay. The technology is still in its early stages, and there is no agreed-upon description of what it is or what it signifies, yet it is one of the most important technologies for organisations.
This blog will help you understand more about this technology and how it may help your business.

So, What Exactly is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is the next step in the evolution of the Internet, and it’s coming fast. This is not something that will occur in the near future. Web 3.0 has already begun to take shape, and it will be completely implemented over the next two years.
Blockchain technology is the main reason behind Web 3.0. Blockchain is the technology that underpins Bitcoin. It is a decentralised ledger technology (DLT) that keeps data across thousands of computers at once rather than just one. This enables greater data storage and exchange, making it more efficient and available to anybody who requires it.
Let’s check Web evolution from 1.0 to 3.0
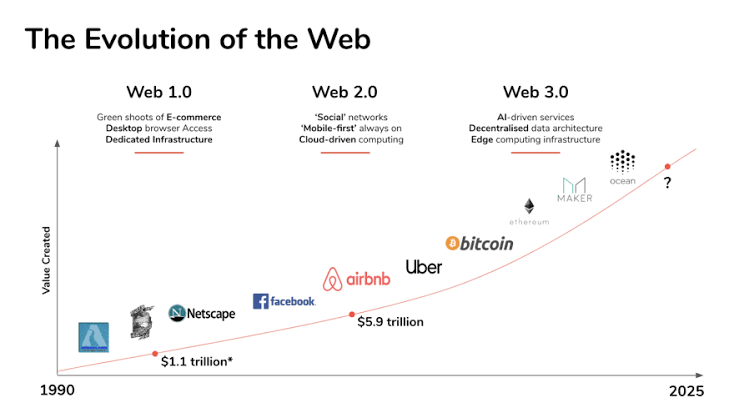
Web 1.0 (1991-2004)
Despite only providing access to restricted information with little to no user involvement, Web 1.0, also known as the Static Web, was the earliest and most dependable internet in the 1990s. Creating user pages or simply commenting on articles wasn’t a thing back then.
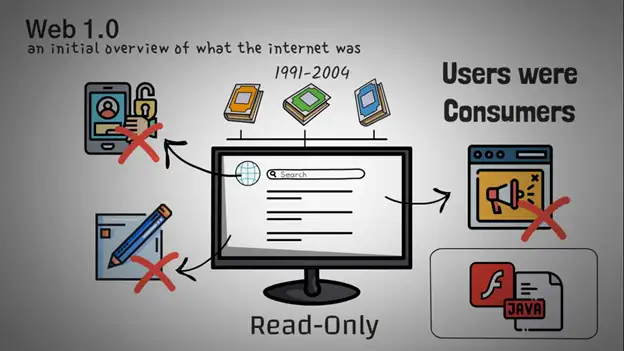
Because there were no algorithms to sift through internet sites in Web 1.0, it was incredibly difficult for consumers to obtain useful information. Simply described, it was like a one-way street with a short walkway where content was created by a select few and information was primarily sourced from directories.
Web 2.0 (2004-Present)
The Social Web, or Web 2.0, made the internet much more interactive due to developments in web technologies such as Javascript, HTML5, CSS3, and others, which enabled companies to establish interactive web platforms such as YouTube, Facebook, Wikipedia, and many more.
In general, Web 2.0 refers to the 21st-century Internet applications that have revolutionized the digital era after the dotcom bubble burst.
This cleared the door for the growth of social networks and user-generated content production, as data can now be transferred and shared across several platforms and apps.

Disadvantages of Current Internet – Web 2.0
The advancement of technology has enabled users to communicate their views and opinions with others, resulting in new ways of organising and engaging with others and promoting a higher level of cooperation.
However, there are several drawbacks to the Internet operating more like an open forum. We have observed a spike in online stalking, cyberbullying, identity theft, and other online crimes as social media has grown globally. Misinformation can also spread among users, whether through open-source information sharing platforms or social media.
Web 3.0 (The Future)
Web 3.0 is the next stage of web evolution that will make the internet highly intelligent which will be able to process information with near-human-like intelligence by using the power of AI systems to run smart algorithms to aid users.

According to Tim Berners-Lee, the Semantic Web is intended to “automatically” interface with systems, people, and home gadgets. As a result, both humans and robots will be involved in the content development and decision-making processes. This would allow for the intelligent distribution of information of highly personalised information directly to each internet user.
Web 3.0’s Key Characteristics
To truly comprehend the next stage of the internet, we must examine the four major elements of Web 3.0:
- Ubiquity
- Semantic Web
- Artificial Intelligence
- 3D Graphics
Ubiquity
Being or having the ability to be everywhere, especially at the same time, is referred to as ubiquity. To put it another way, ubiquitous.
Web 3.0 simply takes this a step further by making the internet available to everyone, at any time and from any location. At some point, internet-connected devices will no longer be limited to computers and smartphones, as they were in Web 2.0, since IoT (Internet of Things) technology will enable the development of a multitude of new sorts and range of smart gadgets.
Semantic Web
The study of the relationship between words is known as semantic(s). As a result, Semantic web allows computers to evaluate massive amounts of data from the Web, such as content, transactions, and relationships between people. For Example,
- I love scuba diving.
- I <3 Scuba-Diving
Their syntax may change, but their semantics are nearly same, because semantics solely addresses the meaning or emotion of the material.
By analysing data, semantics on the Web would allow AI to decipher meaning and emotions. As a result of improved data connectivity, internet users will enjoy a better experience.
Artificial Intelligence
According to Wikipedia, artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence displayed by machines.
And, because Web 3.0 algorithms can read and comprehend the meaning and emotions represented by a set of data, intelligent machines emerge. Although Web 2.0 has comparable characteristics, it is still mostly human-based, which results in biased product evaluations, manipulated ratings, and so on.
For example, a firm might simply assemble a huge number of individuals and pay them to write great reviews for their undeserved products. As a result, in order to deliver accurate data, the internet need AI to learn how to discriminate between the real and the fraudulent reviews.
When it detected efforts at rating manipulation, Google’s AI system erased around 100,000 reviews from the Play Store. This is AI in action, which will soon be integrated into Internet 3.0, allowing blogs and other online platforms to crawl through data and personalise it to each user’s preferences. AI will eventually be able to present people with the best filtered and unbiased data available.
Spatial Web and 3D Graphics
Some futurists refer to Web 3.0 as the Spatial Web because it seeks to blur the border between the real world and the digital world by transforming graphics technology, bringing three-dimensional (3D) virtual worlds into a possibility.
Unlike their 2D predecessors, 3D graphics provide a new degree of immersion not just in futuristic gaming applications such as Decentraland, but also in other industries such as real estate, health, e-commerce, and many others.

Web 3.0 will significantly extend the breadth and scope of both human and machine interactions well beyond anything we can now fathom. Facebook (Meta) being ahead of the industry, has already started Metaverse which is explained below. Web 3.0 will allow us to engage with any person or computer on the planet without having to pay a charge to a middleman. From global co-operatives to decentralised autonomous organisations and self-sovereign data marketplaces, this change will open up a whole new world of previously imagined firms and business models.
This is significant because-
- Societies could become more efficient by disintermediating industries, decreasing rent-seeking third parties, and transferring value directly to network users and providers.
- Organizations can become more flexible to change as a result of their new mesh of more adaptable peer-to-peer communication and governance linkages amongst members.
- Humans, businesses, and AI may exchange more data with more privacy and security protections.
- We can future-proof entrepreneurial and investment activity by practically eliminating the platform reliance concerns that we see now.
- We could own our own data and digital footprints by utilising verifiable digital scarcity of data and tokenised digital assets.
What is the Metaverse, and why is it so significant?
The Metaverse, a virtual reality experience that might be the Internet’s replacement.

The Metaverse is a version of the Internet that you can virtually visit. Wearing a VR headset, you’ll explore this new frontier, creating a virtual duplicate of yourself, where you’ll engage with avatar representations of others.
Given its $1 trillion market potential, Meta (previously Facebook) wants to be the first to occupy this new Internet area. However, you will be able to explore several metaverses, not only Meta’s.
Why are Businesses purchasing Digital land?
Corporations are constructing virtual malls, movie theatres, schools, and museums on Decentraland and The Sandbox because they believe it is where you will spend your time in the future.
Samsung just opened its flagship 837X shop in Decentraland, offering digital excursions by duplicating its real-world New York City store location.

In Decentraland, you may own and rent out digital properties similar to actual property, monetizing billboards and stores to advertising.
Businesses are shifting away from Web 2.0 and toward ambient computing, which will rely on immersive wearable technologies. Our cellphones will soon become relics, with mixed-reality headgear serving as a portal to the future.
Want to know what major Brands are currently doing in MetaVerse?
In a Nutshell…
The new internet will offer a more personalised and customised surfing experience, a smarter and more human-like search helper, and other decentralised benefits that are hoped to contribute to the creation of a more egalitarian web. This will be accomplished by empowering each individual user to have full control over their data and by providing a richer overall experience as a result of the multitude of innovations that will be implemented once it is in place.
Almost all of today’s machines, from home appliances like ovens, vacuums, and television to all modes of transportation, will become part of the IoT economy. As the metaverse takes shape, there’s a sense that IoT technology is approaching a milestone in the Internet’s history.
Businesses that don’t comprehend digital ownership will be left behind as decentralising technology sweeps the industry. There are several examples of corporations that have failed to adapt to change throughout history.
In 1995, if you informed a florist, they would sell flowers on the internet. They’d most likely reject you as insane. It’ll only be a matter of time until small company dealers will start a virtual shop in the metaverse.
Web 3.0 is the Internet’s future, and it’s approaching faster than you would imagine.

Super insightful, loved reading this!
Exceptional work!
Quite interesting, kept me hooked!
Very well explained! Information was pretty interesting and insightful!
Very informative and provides insight and hope.
Very helpful 🙂
Insightful
Very helpful ☺️
Very Informative awesome Suchiiii🔥🔥
A good read.
Interesting
Thought-provoking and articulate.
It is really good and informative!!!
Informative and to the point.
It was quite interesting to read this article.
Excellent Work… Informative… Easy to understand…
Very useful stuff.
Really informative
Very informative content
Great article!
Nicely written.
Super Informative!
Good work!
An insightful read!
Very insightful reading! There’s a world of difference between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0, so I can’t help but wonder what we’ll be able to do once we reach Web 4.0!
Very informative and a delightful read.
the future is here!
A very interesting and informative post for everybody who uses internet! Well done!
I was suppose to learn more about Blockchain few years ago and it’s seem it’s time to get down to it finaly. Very interesting topic and the blog has great flow!